
Asynchronous CircuitĪsynchronous logic is more difficult to design and it has some problems compared to synchronous logic. An asynchronous circuit does not require precise timing control from flip-flops. Hence the state change occurs in direct response to changes that occur in primary input lines. Thus synchronous circuits can be divided into clocked and un-clocked or pulsed sequential circuits.Īn asynchronous circuit does not have a clock signal to synchronize its internal changes of the state. In synchronous circuits, the inputs are pulses with certain restrictions on pulse width and propagation delay.
In asynchronous circuits, the state of the device changes in response to changing inputs. In synchronous sequential circuits, the state of the device changes at discrete times in response to a clock signal.
The sequential circuits are classified into two types Pulse Driven: This is a mixture of the two that responds to the triggering pulses. Synchronous (latch mode) sequential circuit: The behavior can be defined from the knowledge of circuits that achieve synchronization by using a timing signal called the clock. Asynchronous (fundamental mode) sequential circuit: The behavior is dependent on the arrangement of the input signal that changes continuously over time, and the output can be changed at any time (clockless).Ĭlock Driven: Synchronous circuits that are synchronized to a specific clock signal. Sequential logic circuits are divided into three categories like following.Įvent-Driven: Asynchronous circuits that can change the state immediately when enabled.
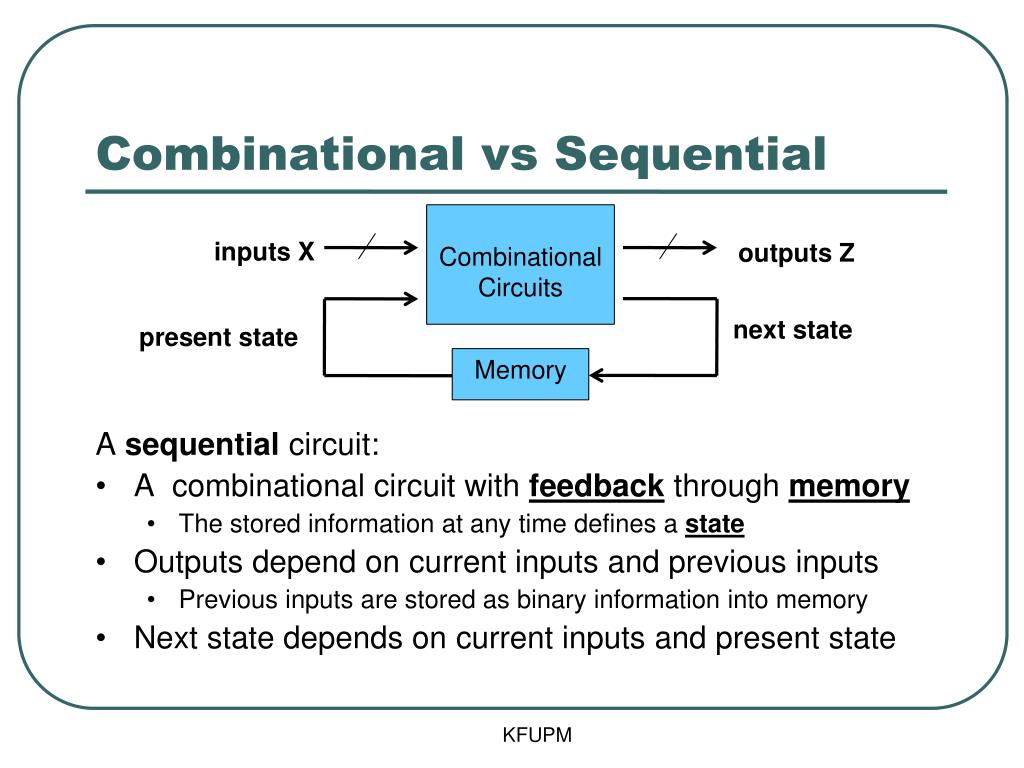
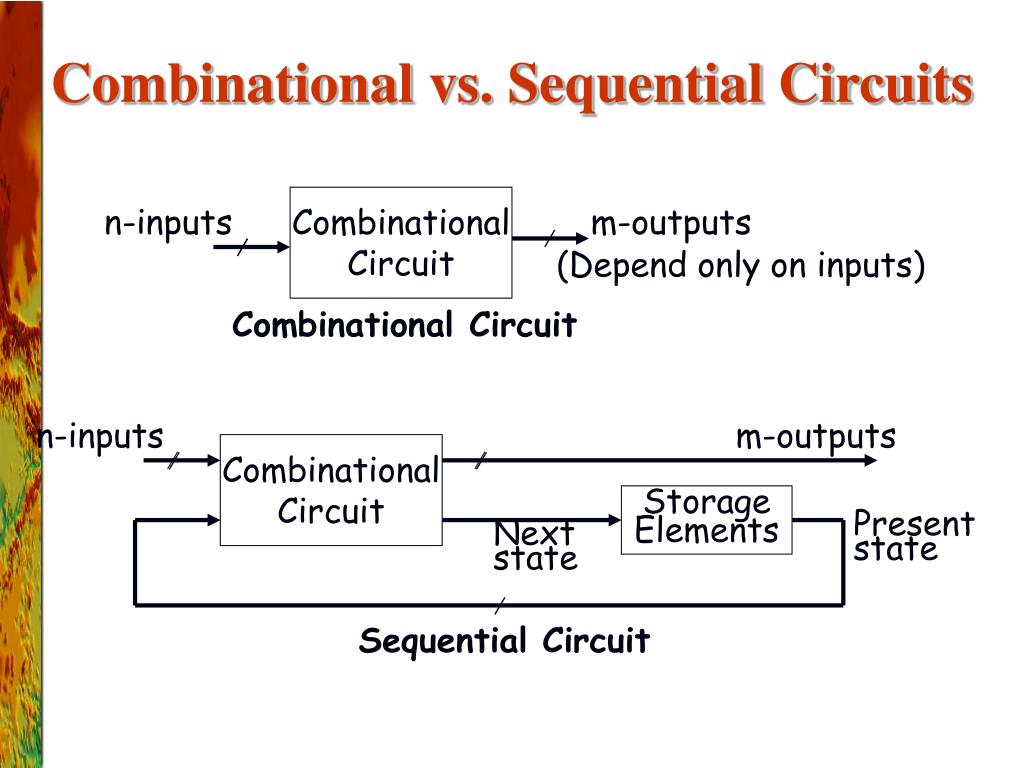
Mathematically speaking, outputs solely depend on the inputs. We can define a combinational logic circuit as an electronic circuit whose outputs depend on the condition that its inputs are in. It is the most basic construction block to add two single-bit numbers. Half adder circuits add two binary single-bit numbers, A and B. This assists in linking the feedback data of the past to current information.Ī half adder can be described as a combinatorial logic circuit with two outputs and inputs. A storing element is included to keep the different data about the stable state levels. The sequential circuit contains memory elements. Registers and Flip Flops are a few examples of sequential circuits.
#Combinational vs sequential circuits full
However, the possibility of a clock is there in the sequential circuit.ĭemultiplexer, decoder, full adder encoder, and half adder are a few examples of combinatorial circuits. There’s no combinational clock present in a circuit. On the other hand, the output of the sequential circuit will depend on the recent outputs and current input. The sequential circuit is a digital circuit type whose output relies not just on the current values of the input signals it has but it depends on the past sequence of inputs as well.Īnother distinction between sequential circuits and combinational circuits is that a memory device is absent in combinational circuits.Īn integrated storage unit for sequential circuits can store instant results.Ī circuit’s output from a combined circuit relies on the input at present. A combinational circuit is a digital circuit type where the output is only a pure function of the present input.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
